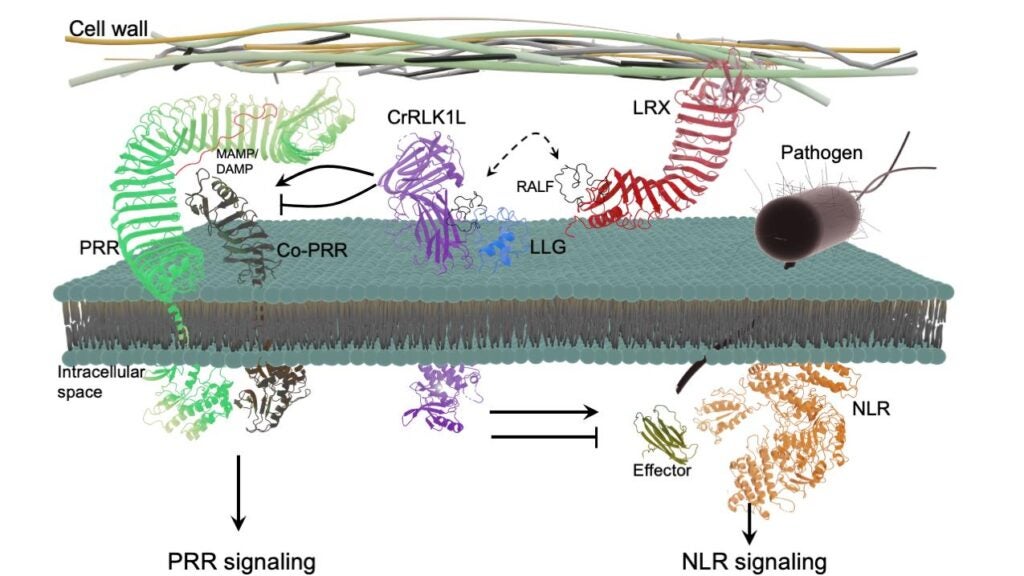
Immune regulators are often crucial in maintaining cellular homeostasis. Defects or over-activation of defense could induce autoimmunity, ultimately leading to cell death. To understand the mechanisms underlying immunity-related cell death, we have developed various RNAi-based screens for cell death suppressors caused by mutations in key immune regulators. This unbiased and highly efficient screen is based on an easy experimental procedure of Agrobacterium-mediated virus-induced gene silencing (VIGS) and a collection of indexed Arabidopsis knockout lines. One screen named “bak to life (BTL)” aims to identify suppressor mutants of cell death due to the loss of the shared PRR coreceptors BAK1 and SERK4. Disruption of a PRR regulated-MAP kinase cascade activates the NLR SUMM2, leading to autoimmunity, which provides a unique case to dissect the intertwined regulation of PRR and NLR activation. Another RNAi screen named “lethality suppressorofmekk1 (LETUM or LET)” identified malectin-like RLKs let1 and LET2, together with GPI-anchored protein LLG1 in the regulation of NLR SUMM2 stability and activation. We are interested in understanding how malectin-like RLKs, also known as Catharanthus roseus receptor-like kinase 1-like kinases (CrRLK1Ls), together with RALF peptide ligands, LLG1, and cell wall-associated leucine-rich repeat extensins (LRXs) in modulating PRR- and NLR-mediated immunity and interaction with fungal pathogens.
Key references:
- Huang, Y., Yin, Y., Liu, J., Feng, B., Ge, D., Kong, K., Ortiz-Morea, F.A., Richter, J., Hauser, M., Wang, W., Shan, L., and He, P.(2020) A trimeric CrRLK1L-LLG1 complex genetically modulates SUMM2-mediated autoimmunity. Nature Communications 11: 4859 | https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-020-18600-8.
- Liu, J., Huang, Y., Kong, L., Yu, X., Feng, B., Liu, D., Zhao, B., Mendes, G.C., Yuan, P., Ge, D., Wang W-M., Fontes, E.P.B, Li, P., Shan, L., and He, P. (2020) The malectin-like receptor-like kinase LETUM1 modulates NLR protein SUMM2 activation via MEKK2 scaffolding. Nature Plants 6: 1106-1115.
- de Oliveira, M.V.V., Xu, G., Li, B., de Souza Vespoli, L., Meng, X., Chen, X., Yu, X., de Souza, S.A., Intorne, A.C., de A. Manhães, A.M.E., Musinsky, A.L., Koiwa, H., de Souza Filho, G.A., Shan, L., and He, P. (2016). Specific control of Arabidopsis BAK1/SERK4-regulated cell death by protein glycosylation. Nature Plants 2: 15218.
